OCR Pytesseract
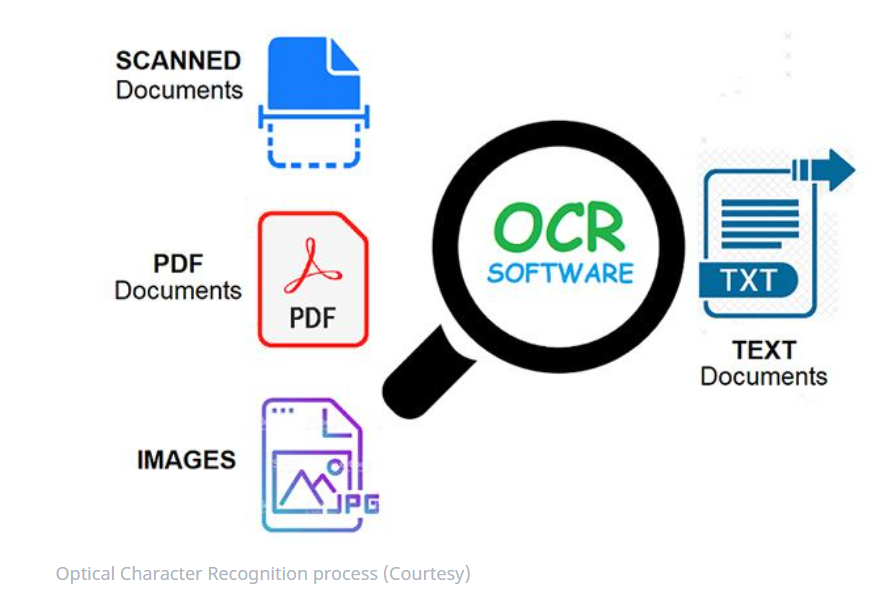
Published: January 17, 2020Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronic or mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene-photo (for example the text on signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed on an image. Source: Wikipedia
In layman terms, OCR is a process of extracting text from a document instead of typing the whole thing yourself.
Document can be in form of PDF’s ,Images or scanned documents .
If we have data stored in form of documents then to do any form of analytics on the text data we need to make use of OCR to extract the data and perform text analytics on that data.
I worked on a Named Entity Recognition problem, where I had a bunch of employee contracts as PDF documents and I needed to extract the below entities form the documents
- Employee Name
- Employer Name
- Salary
- Location
I used OCR to extract the data in text form and applied NER on that data.
Similiarly other data science approcahes could be applied if the data is avaliable in text form.
Py-Tesseract
We will be using python library pytesseract for OCR.
Python-tesseract (pytesseract) is a python wrapper for Google’s Tesseract-OCR.
Python-tesseract is an optical character recognition (OCR) tool for python. That is, it will recognize and “read” the text embedded in images.
from wand.image import Image as IM
from PIL import Image as PIM
from os import listdir
from os.path import isfile, join
import pytesseract
import argparse
import cv2
import os
import pandas as pd
import re
import time
from PyPDF2 import PdfFileWriter, PdfFileReader
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure
start_time = time.time()
Create two folder , one for PDF file and other for images
pdfPath=r"D:\works\OOCR\split_pdf"
imgPath=r"D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg"
Either add tesseract location in an environment variable or pass the location as below
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = r"C:\Program Files (x86)\Tesseract-OCR\tesseract.exe"
os.environ['PATH'] = os.environ['PATH'].encode('utf-8')
OCR on Image
from IPython.display import Image
Image(filename='testOCR.jpg')

Tesseract in Action
img1=PIM.open("testOCR.jpg")
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(img1, lang='eng')
print(text)
Now | am become
Death, the destroyer
of worlds
OCR on PDF file
We will be extract text data from PDF document by following below steps:-
- Read PDF file.
- Split PDF pages into seperate PDF files.
- Convert these indivisual PDF files into images(jpg).
- Apply OCR (pytesseract) on these image and stor these text data in CSV file.
Download the PDF file from web
!curl "https://papers.nips.cc/paper/5021-distributed-representations-of-words-and-phrases-and-their-compositionality.pdf" >> embeddings.pdf
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0
29 109k 29 32768 0 0 32768 0 0:00:03 0:00:01 0:00:02 24674
100 109k 100 109k 0 0 109k 0 0:00:01 0:00:01 --:--:-- 64588
Step 1 : Read PDF file by PDFFileReader
fname="embeddings.pdf"
inputpdf = PdfFileReader(open(fname,"rb"))
print('Number of PDF Pages = '+str(inputpdf.numPages))
Number of PDF Pages = 9
Step 2: Split these pdf pages into separate PDF files
make sure to change the split_f_name variable based on your folder location
The below code will split the pdf file into separate PDF files
for i in range(inputpdf.numPages):
output = PdfFileWriter()
output.addPage(inputpdf.getPage(i))
with open(pdfPath+"\\"+fname[:fname.find('.')]+'_'+str(i)+'.pdf', "wb") as outputStream:
output.write(outputStream)
List of created PDF
[f for f in listdir(pdfPath) if isfile(join(pdfPath, f))]
['embeddings_0.pdf',
'embeddings_1.pdf',
'embeddings_2.pdf',
'embeddings_3.pdf',
'embeddings_4.pdf',
'embeddings_5.pdf',
'embeddings_6.pdf',
'embeddings_7.pdf',
'embeddings_8.pdf']
Step 3: Convert PDF files to images
%%time
pdffiles = [f for f in listdir(pdfPath) if isfile(join(pdfPath, f))]
for pdfName in pdffiles:
print "Converting PDF file" ,pdfName,"to Image..."
imgfname=imgPath+"\\"+pdfName[:pdfName.find('.')]+".jpg"
print "Creating Image" ,imgfname,"..."
print("="*50)
with(IM(filename=pdfPath+"\\"+pdfName,resolution=200)) as source:
images=source.sequence
pages=len(images)
IM(images[i]).save(filename=imgfname)
Converting PDF file embeddings_0.pdf to Image...
Creating Image D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg\embeddings_0.jpg ...
==================================================
Converting PDF file embeddings_1.pdf to Image...
Creating Image D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg\embeddings_1.jpg ...
==================================================
Converting PDF file embeddings_2.pdf to Image...
Creating Image D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg\embeddings_2.jpg ...
==================================================
Converting PDF file embeddings_3.pdf to Image...
Creating Image D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg\embeddings_3.jpg ...
==================================================
Converting PDF file embeddings_4.pdf to Image...
Creating Image D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg\embeddings_4.jpg ...
==================================================
Converting PDF file embeddings_5.pdf to Image...
Creating Image D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg\embeddings_5.jpg ...
==================================================
Converting PDF file embeddings_6.pdf to Image...
Creating Image D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg\embeddings_6.jpg ...
==================================================
Converting PDF file embeddings_7.pdf to Image...
Creating Image D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg\embeddings_7.jpg ...
==================================================
Converting PDF file embeddings_8.pdf to Image...
Creating Image D:\works\OOCR\img_jpg\embeddings_8.jpg ...
==================================================
Wall time: 7.77 s
List of created Images
[f for f in listdir(imgPath) if isfile(join(imgPath, f))]
['embeddings_0.jpg',
'embeddings_1.jpg',
'embeddings_2.jpg',
'embeddings_3.jpg',
'embeddings_4.jpg',
'embeddings_5.jpg',
'embeddings_6.jpg',
'embeddings_7.jpg',
'embeddings_8.jpg']
Step 4: Applying OCR on Images
%%time
contentDict={}
Imgfiles = [f for f in listdir(imgPath) if isfile(join(imgPath, f))]
for ImgName in Imgfiles:
print "Reading Image",ImgName,'...'
img1=PIM.open(imgPath+"\\"+ImgName)
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(img1,lang='eng')
contentDict[ImgName]=text
Reading Image embeddings_0.jpg ...
Reading Image embeddings_1.jpg ...
Reading Image embeddings_2.jpg ...
Reading Image embeddings_3.jpg ...
Reading Image embeddings_4.jpg ...
Reading Image embeddings_5.jpg ...
Reading Image embeddings_6.jpg ...
Reading Image embeddings_7.jpg ...
Reading Image embeddings_8.jpg ...
Wall time: 3min 31s
contentDict["embeddings_0.jpg"][:500]
u'Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases\nand their Compositionality\n\nTomas Mikolov Ilya Sutskever Kai Chen\nGoogle Inc. Google Inc. Google Inc.\nMountain View Mountain View Mountain View\nmikolov@google.com ilyasu@google.com kai@google.com\nGreg Corrado Jeffrey Dean\nGoogle Inc. Google Inc.\nMountain View Mountain View\ngcorrado@google.com jeff@google.com\nAbstract\n\nThe recently introduced continuous Skip-gram model is an efficient method for\nlearning high-quality distributed vector representati'
from IPython.display import Image
Image(filename=imgPath+"\\"+"embeddings_0.jpg")

Reading data in a dataframe
df=pd.DataFrame(contentDict.items(), columns=['FileName', 'TextContent'])
df
| FileName | TextContent | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | embeddings_5.jpg | Newspapers\nNew York New York Times Baltimore ... |
| 1 | embeddings_7.jpg | Model Redmond Havel ninjutsu graffiti capitula... |
| 2 | embeddings_1.jpg | Input projection output\n\n \n\nw(t-2)\nif\n/ ... |
| 3 | embeddings_3.jpg | Country and Capital Vectors Projected by PCA\n... |
| 4 | embeddings_8.jpg | References\n\n1] Yoshua Bengio, Réjean Ducharm... |
| 5 | embeddings_4.jpg | Method Time [min] | Syntactic[%] Semantic [%] ... |
| 6 | embeddings_6.jpg | NEG-15 with 10~° subsampling\n\nHS with 10~° s... |
| 7 | embeddings_0.jpg | Distributed Representations of Words and Phras... |
| 8 | embeddings_2.jpg | training time, The basic Skip-gram formulation... |
Let’s try to build a word cloud to quickly understand the document
def fxn_wordcloud(inp_val):
text = inp_val
wordcloud = WordCloud().generate(text)
figure(num=None, figsize=(15, 7), dpi=80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
plt.imshow(wordcloud, interpolation='bilinear')
plt.show()
data=df.loc[df.FileName=='embeddings_0.jpg','TextContent'].values[0]
data[:300]
u'Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases\nand their Compositionality\n\nTomas Mikolov Ilya Sutskever Kai Chen\nGoogle Inc. Google Inc. Google Inc.\nMountain View Mountain View Mountain View\nmikolov@google.com ilyasu@google.com kai@google.com\nGreg Corrado Jeffrey Dean\nGoogle Inc. Google Inc.\nMount'
fxn_wordcloud(data)

Conclusion
In this post, we learned how to apply OCR on images and PDF documents and use that data in text analytics like word cloud to quickly gain insight about the document. At times there might be some spelling mistake or gibberish output text, so please check the data before using it. On some occasions OCR was unable to read some PDF files.
References
https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2017/07/10/using-tesseract-ocr-python/
https://pypi.org/project/pytesseract/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13984357/pythonmagick-cant-find-my-pdf-files/
https://glenbambrick.com/tag/pythonmagick/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41353360/unable-to-install-pythonmagick-on-windows-10/

Leave a comment